Marketing is the art and science of connecting products, services, and ideas to the right people at the right time. For businesses of all sizes, marketing is essential for growth, customer engagement, and long-term success. This article covers the fundamentals of marketing, including strategies, principles, and tools to help you understand how marketing works and how you can apply it effectively.
1. What is Marketing?
Marketing encompasses all the activities a company undertakes to promote, sell, and distribute products or services. It goes beyond just advertising or sales – it’s about understanding customer needs, creating value, and building strong relationships. At its core, marketing helps businesses to:
- Identify and understand customer needs.
- Develop products or services that meet these needs.
- Promote offerings effectively to attract and retain customers.
- Build brand loyalty and long-term customer relationships.
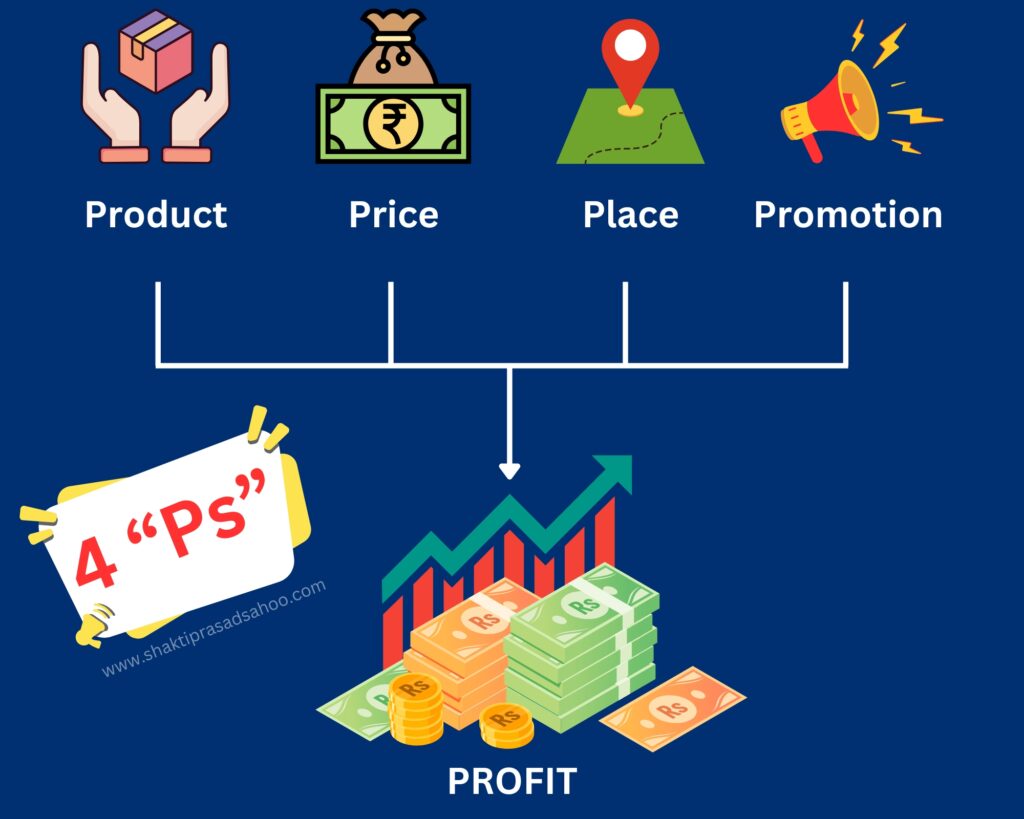
2. The 4 Ps of Marketing
The “4 Ps” are a framework for developing an effective marketing strategy. Also known as the Marketing Mix, these elements are:
- Product: What are you offering to the market? The product or service should fulfil a need or solve a problem for the customer. Understanding the product’s lifecycle, features, benefits, and unique selling points (USP) is key.
- Price: This is the cost the customer pays. Pricing strategies are vital because they directly impact demand, profit margins, and customer perception. Pricing should consider factors like production costs, competitor pricing, and perceived value.
- Place: Where are you selling your product? This covers distribution channels – online, retail, direct sales, etc. Choosing the right place ensures that your product reaches the target audience effectively and efficiently.
- Promotion: How do you communicate the benefits of your product? This involves advertising, public relations, social media, email marketing, and sales strategies that raise awareness and generate interest in the product.
3. The Importance of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation divides the target market into smaller groups based on shared characteristics, such as demographics, psychographics, behaviour, or geography. Segmentation helps businesses to:
- Tailor marketing messages to specific groups.
- Allocate resources efficiently by targeting only those likely to buy.
- Improve customer experience by meeting the needs of different segments.
Example Segmentation Strategies:
- Demographic Segmentation: Age, gender, income, education level.
- Behavioural Segmentation: Purchase behaviour, usage rate, brand loyalty.
- Geographic Segmentation: Location-based targeting for localized marketing.
4. Understanding the Customer Journey
The customer journey is the process a customer goes through from awareness to purchase and beyond. It includes the following stages:
- Awareness: The customer becomes aware of the product or brand.
- Consideration: The customer researches and evaluates options.
- Decision: The customer decides to purchase.
- Retention: The customer becomes a loyal user, possibly repurchasing or engaging with the brand.
- Advocacy: The customer recommends the brand to others, acting as a brand ambassador.
Mapping the customer journey helps businesses to provide relevant content, engage customers at the right time, and improve overall satisfaction.
5. Branding and Positioning
Branding is the process of creating a unique image and identity for a product or service. It’s about defining what your business stands for and how it’s perceived by the public. Key elements of branding include:
- Brand Identity: The visual and verbal elements, such as logo, tagline, colours, and messaging.
- Brand Positioning: How you want customers to perceive your brand relative to competitors.
- Effective branding creates a lasting impression, drives customer loyalty, and can be a deciding factor for customers in a competitive market.
6. Marketing Channels and Tools
In today’s digital age, there are numerous channels and tools to reach your audience:
- Digital Marketing: Channels like social media, email marketing, content marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and paid advertising.
- Traditional Marketing: Television, radio, print advertising, and direct mail, which still hold value, especially for reaching older demographics or local markets.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable, informative, or entertaining content to attract and retain customers. This can include blog posts, videos, eBooks, and infographics.
Marketing Automation Tools such as Mail Chimp, HubSpot, or Google Analytics can also help streamline tasks, track performance, and personalize communication.

7. The Role of Data in Marketing
Data is at the heart of modern marketing, providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and engagement. By analyzing data, marketers can:
- Measure the effectiveness of campaigns.
- Identify which channels and messages resonate most with audiences.
- Make informed decisions to improve ROI.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rate, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value are essential metrics for tracking success and optimizing strategies.
8. Creating a Marketing Strategy
A well-defined marketing strategy aligns with the business goals and sets a roadmap for achieving them. Key steps in creating a strategy include:
- Setting Clear Goals: Define measurable objectives (e.g., increase sales by 20%).
- Defining Target Audience: Know who you’re trying to reach.
- Selecting Channels: Choose the platforms and media that best reach your audience.
- Budget Allocation: Determine the budget for each campaign.
- Continuous Optimization: Regularly analyse and adjust strategies based on performance.
9. The Importance of Testing and Analytics
Testing different approaches helps businesses identify what works best. A/B testing, for example, allows you to compare two versions of a campaign to see which performs better. Analytics tools, like Google Analytics and social media insights, help you understand which tactics drive the best results.
10. Staying Up-to-Date with Marketing Trends
Marketing is constantly evolving. Staying up-to-date with trends, especially in digital marketing, is essential. Trends in AI, voice search, and personalization are shaping the future of marketing, making it essential for marketers to be agile and adaptable.
Conclusion
The basics of marketing lay the foundation for any successful business strategy. From understanding the 4 Ps and customer journey to leveraging data and modern marketing tools, these principles provide a roadmap to effectively reach and engage customers. By mastering these fundamentals, businesses can create lasting connections, drive sales, and build strong brand loyalty.